The continually increasing number of EVs is driving demand for more charging points, therefore creating the need for more charging infrastructure where smart charging networks have a fundamental role.
As buildings want to expand their EV charging infrastructure and need to provide energy to more charging points, they may encounter limitations in their electrical capacity. Moreover, electrical upgrades can be expensive, and your budget might need to be optimised.
This is where Energy Management Solutions comes in handy, allowing you to maximise the energy efficiency of your EV installation and increasing the number of EV chargers you can install without making costly electrical upgrades.
What is Static Load Management?
Power sharing is a charger-based feature that allows you to maximise the number of chargers for your parking installation without major electrical upgrades by balancing the available electricity between plugged-in EVs.
Available energy is intelligently distributed across all chargers requesting current to ensure everybody can charge as fast as possible without exceeding the electrical constraints of your installation. Depending on the model of your Wallbox, you can create a network of up to 25 Chargers (Pulsar Plus, Copper SB or Commander 2) or even more with Pulsar Max.
Static Load Management benefits multi-charger installations, such as workplaces, fleet depots, apartment condos and parking lots.
How does Static Load Management work?
In a Static Load Management network, the installer is required to introduce the electrical constraints of the installation. A Primary charger is established, and this charger determines how much electrical current each other installed chargers are allocated at a given time. The other installed chargers, called the “Secondaries”, will always follow the “Primary”.
You can find more information about this feature setup in our EMS Installation guide.
Once the network is set up and installed accordingly, Static Load Management will ensure equal distribution of available power between the Wallbox chargers that require current until the maximum power constraint is reached or all chargers are using the maximum available power.
To illustrate, suppose you would like to electrify four parking spots while optimising your EV charging installation of 60A.
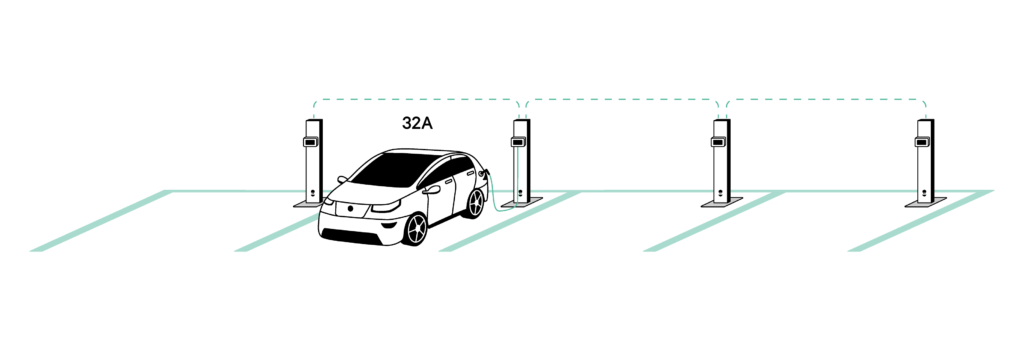
- A first vehicle can begin charging at maximum capacity, using 32A of the available 60A (figure 1).
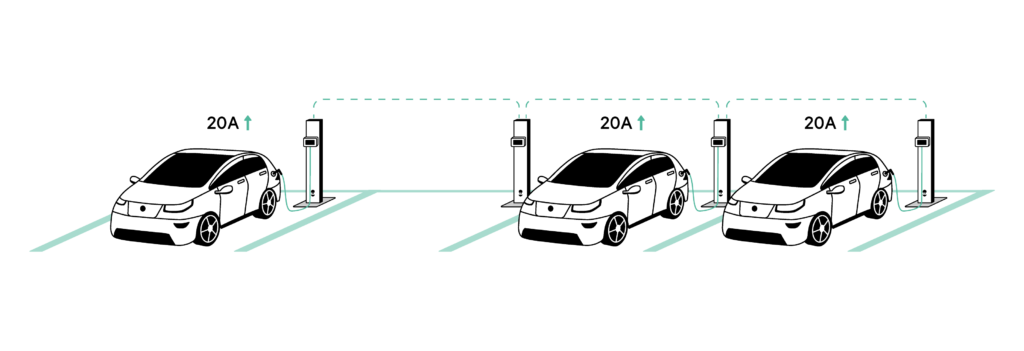
- When second, third and fourth EVs start charging, Static Load Management allows the power to be balanced between all chargers. This ensures all available current is used and shared equally between EVs, using 60A of the available 60A (figure 2).
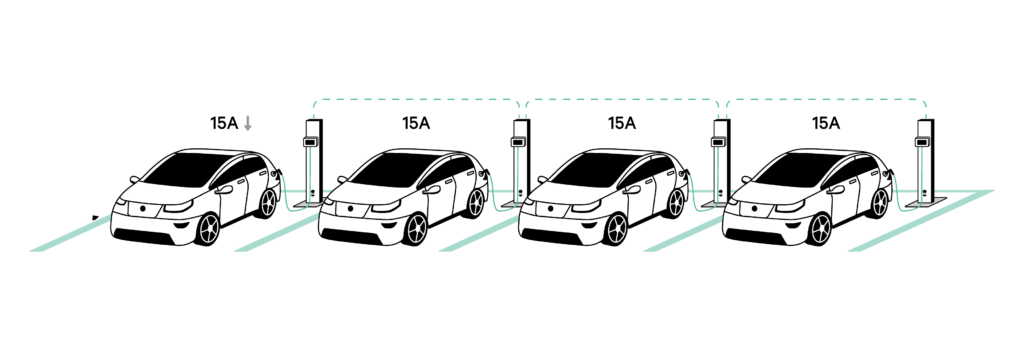
- The second vehicle finishes charging as its battery is full or because the EV has been unplugged. This naturally frees up more available current for the remaining vehicles still charging. Static Load Management re-distributes the newly available power between the vehicles to ensure the rest of the vehicles charge as fast as possible, using all 60A of the available 60A again (figure 3).
What is the difference with Dynamic Static Load Management?
Another Wallbox EMS is Dynamic Static Load Management (DPS). DPS monitors a building’s demand and compares it to its maximum allowable value. When it is lower than the maximum, DPS can supply all the remaining available power to reach the maximum allowed to the charging network to ensure the charging network is balanced against the building’s load.
By taking advantage of periods with low demand from the building side, the charging network’s demand can be satisfied without increasing the installation’s overall power.
To go further
If you are interested in optimising the energetic performances of your charging infrastructure, or if you intend to expand your current network, you should also consider Phase Rotation and read our article.
If you need more information on how to design a multi-charger installation or have questions about Static Load Management, you can contact us via our contact form and our experts will advise you on the best available solutions.